|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Memory: levels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
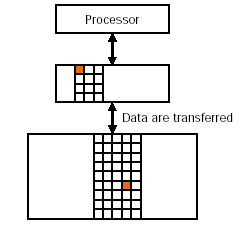
Data is transferred only
between adjacent levels: |
|
|
|
When miss occurs at one
level of hierarchy, data is transferred from next lower level |
|
|
Minimum unit of data
transferred: block |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Performance depends on
speed of hits and misses |
|
|
|
|
Hit time: time to access upper level, |
|
|
|
|
|
including determining hit
or miss |
|
|
|
|
|
Miss penalty: time to access lower level to get data |
|
|
|
Issues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
How much data to transfer
between levels |
|
|
|
|
Policy to replace data in
upper levels |
|
|
|
|
Policy to update data in
each level |
|
|
|
Analogy |
|
|
|
|
|
Need 10 books for a term
paper |
|
Fig. 7.2 |
|
|
|
|
Bring all 10 books back
to your desk, |
|
|
|
|
|
instead of going back to
library 10 times |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

