A spatial data structure is one which is capable of storing
and sorting objects based on multidimensional
keys. The two-dimensional
structures, such as the PR quadtree and PM quadtrees, can store objects
based on two values, such as the longitude and latitude (x, y) of a
city. In Java this is not a big deal, but in other languages, such as
C and C++, it is.
Note that latitude lines are horizontal, north and south of
the equator, and correspond to lines with a fixed y coordinate, such
as 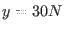 . Longitude lines are
vertical, east and west of Greenwich, England, and correspond to lines with a fixed x coordinate,
such
. Longitude lines are
vertical, east and west of Greenwich, England, and correspond to lines with a fixed x coordinate,
such 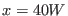 .
Three-dimensional structures, such as a K-d tree of order 3 or a PM octree, can
store objects based on three values, such as the longitude, latitude, and
sea level of a city (x, y, z).
.
Three-dimensional structures, such as a K-d tree of order 3 or a PM octree, can
store objects based on three values, such as the longitude, latitude, and
sea level of a city (x, y, z).
MM Hugue
2019-03-03