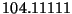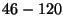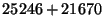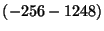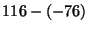Next: About this document ...
Name:
SSN(6):
CMSC 311 Computer Organization
Jolly Numbers Worksheet with Answers
-draft-
-NO CALCULATORS-
Fall, 1999
Dr. Hugue
- Write the decimal number,
 , as an unsigned binary number. Express
your answer in hexadecimal and octal as well.
, as an unsigned binary number. Express
your answer in hexadecimal and octal as well.
Answer: 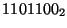 ,
,  ,
, 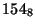
- Write the hexadecimal number,
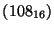 , as a decimal number.
, as a decimal number.
Answer: 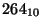
- What is the largest integer (in decimal) that can be expressed as a
32-bit unsigned binary number? Note: as always, you may express your
answer in terms of powers of two if you like.
Answer:
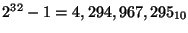
- Write the decimal number
 as a 16-bit sign magnitude
number. Express your answer in hexadecimal as well.
as a 16-bit sign magnitude
number. Express your answer in hexadecimal as well.
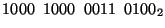 ,
, 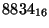
- Express the hexadecimal number
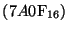 as a base 10 number,
assuming that the original hexadecimal number is in sign magnitude form.
Repeat assuming unsigned binary form.
as a base 10 number,
assuming that the original hexadecimal number is in sign magnitude form.
Repeat assuming unsigned binary form.
Answer:
Sign magnitude:

Unsigned Binary:

- Express the hexadecimal number
 as a base 10 number,
assuming that the original hexadecimal number is in sign magnitude
form. Repeat assuming unsigned binary form.
as a base 10 number,
assuming that the original hexadecimal number is in sign magnitude
form. Repeat assuming unsigned binary form.
Sign magnitude:

Unsigned Binary:
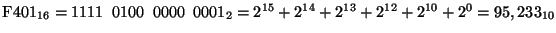
- Convert the following ``decimal fractions'' to 32-bit fixed point
equivalents, where the ``binary fraction'' is the lower
16 bits, and the ``binary
integer'' part is the upper 16 bits. The ``binary integer'' part is stored
as a sign magnitude number. You may give your answer in hexadecimal for
convenience. Also indicate which representations are exact, and which are
approximations because of truncations. Is underflow present anywhere?


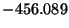

-
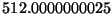

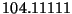



- Express the fixed-point numbers above using 32-bit IEEE floating-point notation.

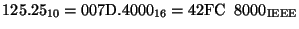
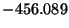

-
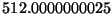
 (with rounding)
(with rounding)
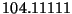



- Express both operands in signed 2's complement, and perform the
indicated operations. (Note: don't forget to sign-extend the numbers so
that all arithmetic is performed between numbers of the same size.)
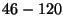
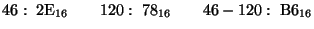
-

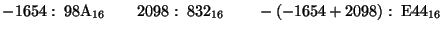
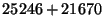

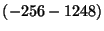
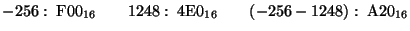
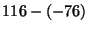
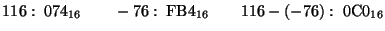
- Which of the operations in the previous problem, if any, can be
performed correctly using 16-bit signed 2's complement arithmetic.
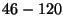
Yes
-

Yes
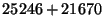
No
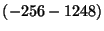
Yes
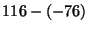
Yes



Next: About this document ...
MM Hugue
2004-09-08

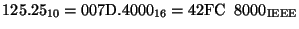
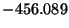

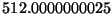
 (with rounding)
(with rounding)