| Finite state machines: implementing | |||||||||||||||
| q1 | q0 | x | q1+ | q0+ | z | 
|
|||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | d | d | d | ||||||||||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | d | d | d | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||||
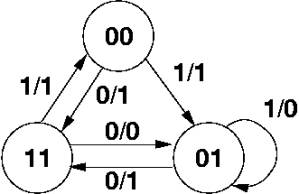
| In state 01, input of 0 gives state 11 and output 1 | |||||||||||||||
| In state 01, input of 1 gives state 01 and output 0 | |||||||||||||||
| In state 11, input of 0 gives state 01 and output 0 | |||||||||||||||
| In state 11, input of 1 gives state 00 and output 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Rest of steps: | |||||||||||||||
| - pick flip-flops | |||||||||||||||
| - use excitation tables | |||||||||||||||
| - draw circuit (ROM, gates, or PLA) | |||||||||||||||