|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flip-flops |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic building blocks |
|
|
|
|
|
Combinational circuits:
gates |
|
|
|
|
Sequential circuits:
flip-flops |
|
|
|
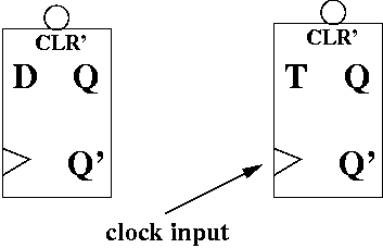
Examples of flip-flops |
|
|
|
|
State: flip-flop stores 1
bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inputs: |
control (D or T) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
clock (positive edge) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output: |
Q and Q' (negation) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q is current state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Why both Q and Q'? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Because we can! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flip-flops
can be built with NOR and NAND gates, and the negated output is |
|
|
|
|
|
essentially free |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional input (rarely
drawn) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLR': asynchronous clear |
|
|
|
|
|
|
When set to 0, Q is
immediately (asynchronously) set to 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
This is called active low
(consumes less power) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

