|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sequential circuits:
clock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"Without time,
everything would happen at once." |
|
|
- Anonymous |
|
|
|
Clock |
|
|
|
|
Outside world: way to tell time |
|
|
|
|
Computer: think of a
metronome (number of beats, or cycles, per minute) |
|
|
|
Measured in MHz or Ghz
(millions or billions of cycles per second) |
|
|
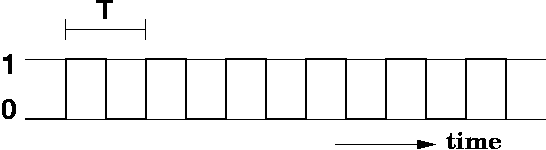
Timing diagram |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x-axis: time |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y-axis: voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
values 0 and 1 are
represented by low and high voltage |
|
|
|
|
A clock is a device which
alternates values between 0 and 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
period: time T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cycle: single alternation
between 0 and 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
frequency: f = 1/T, units
of Hz (cycles per second) |
|
|
|
|
1 GHz means 109 cycles per second |
|
|
|
|
|
(period is 10-9 seconds, which is 1
nanosecond) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

