|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gates: XOR properties |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Truth table: |
|
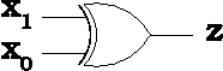
Symbol: |
|
|
|
Input |
|
Output |
|
|
|
|
x0 |
x1 |
z |
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XOR can be expressed in
terms of AND, OR, NOT: |
|
|
|
|
|
x XOR y == ( x AND (NOT
y) ) OR ( (NOT x) AND y ) |
|
|
|
|
|
(If x is true, y must be
false, and vice versa.) |
|
|
|
|
x0 ^ x1 ^ . . . xn |
is true if the number of
true values is odd, |
|
|
|
|
and false if the number of true values is
even. Why? |
|
|
|
|
x0 ^ x1 ^ . . . xn == (x0 + x1 + . . . xn) % 2 |
|
|
|
|
XOR is the same as the
sum modulo 2 |
|
|
|
|
x ^ 0 = x |
|
XORing with 0 gives you
back the same number (identity) |
|
|
|
x ^ 1 = ~x |
|
XORing with 1 gives you
the complement |
|
|
|
|
x ^ x = 0 |
|
XORing a number with
itself gives 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

