As you already know, a user process in GeekOS is a Kernel_Thread with an attached User_Context. Each Kernel_Thread has a field alive that indicates whether it has terminated (e.g., whether Exit() has been called). A Kernel_Thread also has a refCount field that indicates the number of kernel threads interested in this thread. When a thread is alive, its refCount is always at least 1, which indicates its own reference to itself. If a thread for a process is started via Start_User_Thread with a detached argument of "false", then the refCount will be 2: one self-reference plus a reference from the owner. When detached is false, the owner field in the new Kernel_Thread object is initialized to point to the Kernel_Thread spawning it (aka the parent). Typically, the parent of a new process is the shell process that spawned it.
The parent-child relationship is useful when the parent wants to retrieve the returned result of the new process using the Wait() system call. For example, in the shell (src/user/shell.c), if Spawn_Program is successful, the shell waits for the newly launched process to terminate by calling Wait(), which returns the child process's exit code. The Wait system call is implemented by using thread queues, which we explain below.
When a process terminates by calling Exit, it detaches itself, removing its self-reference. Moreover, when the parent calls Wait, it removes the other reference, bring refCount to 0. When this is the case, the Reaper process is able to destroy the thread, discarding its Kernel_Thread object.
Any process that is dead, but has not been reaped, is called a zombie. The reasons for this could be many, one instance being the parent failing to release its refCount: bug or otherwise.
This process is a zombie that's "totally dead," as the child has called Exit to reduce its refCount, and if it had a parent at all, the parent reduced its refCount too. Thus, the process will soon be reaped.
The process has called Exit(), but the parent hasn't called Wait(). In this case, the process is also a zombie, but is not on the graveyard queue.
The process is a detached background process, and is alive.
The process is a "foreground" process, and is alive.
In the first two cases, the process eventually switches from the
waiting state to the ready state and is then removed from its I/O queue
and put back in the run
queue. A process continues this cycle until it terminates, at which
time it is not present on any queue.
$ null.exe &
[10]
$
It could be that once a process starts to run, it may behave badly,
or the work it is performing may
become irrelevant. Therefore, we would like to have some way for
one process to kill another process. To do this, do the following:
Implement the Sys_Kill() system call (a stub appears in src/geekos/syscall.c) that takes a PID as its first argument and a dummy number as its second. (We will eventually use that argument to send signals in a later project.) The given process should be killed immediately. (This is unsafe in a general setting, since that process might hold shared resources, but there aren't any shared resources in GeekOS. Yet.).
This is different from a thread calling Exit(). Note that when a thread is executing it is not in any queue and is only referenced in g_currentThread. Therefore when doing the cleanup of a thread that called Exit by itself it makes sense to not consider any queues. But an asynchronous kill of a process can happen at any time. Particular example scenarios are for instance when the process is waiting for its child process to die and so is in the wait queue for that process. Or when it is in the runQueue of the system. Therefore when doing this asynchronous kill you will need to ensure that you properly remove the process from all queues it is in.
Also consider what should happen with a killed process's child processes: Their parent pointer is now invalid, and so they should be adjusted accordingly. Indeed, the same thing should happen for Exit, but does not in the implementation we provide---it turns out that this field is not used by the child process after its parent dies, so it can be left dangling. However, in your modified code, you will be using the parent pointer to print the process table, so both Exit and Kill should behave similarly, nulling the dangling parent pointer.
There is an interesting design point here: if a parent dies and fails to Wait() on its children, should we also decrement the children's refCount? If this does not happen, the child will remain a zombie, so decrement the counter.
When determining which processes can be killed; a process that falls in category II above (sec "More about process lifetimes: Zombies") should be allowed to be killed. This would happen because a child has died but its parent has not yet done a Sys_Wait, and we want Sys_Kill to be able to clean up the system nonetheless.
Don't kill kernel processes.
A process may kill itself; this is unlikely to be tested because it is a dumb substitute for calling Exit().
Now that we can run many processes from the shell at once, we might like to get a snapshot of the system, to see what's going on. Therefore, you will implement a program and a system call that prints the status of the threads and processes in the system:
struct Process_Info {
char name[128];
int pid;
int parent_pid;
int priority;
int status;
};
Here, pid and parent_pid should be self-explanatory. The "name"
part is the program argument to Spawn() (not the command argument); for kernel processes
this should be "{kernel}". The "status" field should be 0
for runnable threads (ie threads that are in the runQueue or actually
running), 1 for blocked (ie threads that are waiting on some I/O queue,
or the queue of a child process), and 2 for zombie (ie threads that are
no longer alive but have not yet been reaped). The proper
#defines for these, and the above struct, are in
include/geekos/user.h, which is included by
include/libc/process.h. Finally, priority is the scheduling priority number
of the
process. You can get this information
from the Kernel_Thread and User_Context structs, though you may need
to augment them.When printing out the status of the process, it should be considered a zombie if it falls in category 1 or 2 above (in sec "More about process lifetimes: Zombies") ---that is, a process is a zombie if the alive field is false.
PID PPID PRIO STAT COMMANDThe PS system call stub in user space has been defined for you; its prototype appears in include/libc/process.h. Your process table must have space for at least 50 entries. Please use "%3d %4d %4d %4c %s" as the format string to achieve the formatting in the table as shown. Failure to use the format string may cause tests to fail.
1 0 1 B {kernel}
2 0 1 R {kernel}
3 0 1 B {kernel}
4 0 1 B {kernel}
5 0 1 B {kernel}
6 1 2 B /c/shell.exe
7 0 1 B /c/forktest.exe
8 7 2 R /c/null.exe
9 7 2 R /c/null.exe
10 7 2 R /c/null.exe
Privilege levels range from 0 to 3. Level 0 processes have the most privileges, level 3 processes have the least. Protection levels are also called rings in 386 documentation. Kernel processes in GeekOS run in ring 0, user processes run in ring 3. Besides limiting access to different memory segments, the privilege level also determines the set of processor operations available to a process. A program's privilege level is determined by the privilege level of its code segment.
If a process attempts to access memory outside of its legal segments, the result should be the all-too-familiar segmentation fault, and the process will be halted.
Another important function of memory segments is that they allow programs to use relative memory references. All memory references are interpreted by the processor to be relative to the base of the current memory segment. Instruction addresses are relative to the base of the code segment, data addresses are relative to the base of the data segment. This means that when the linker creates an executable, it doesn't need to specify where a program will sit in memory, only where the parts of the program will be, relative to the start of the executable image in memory.
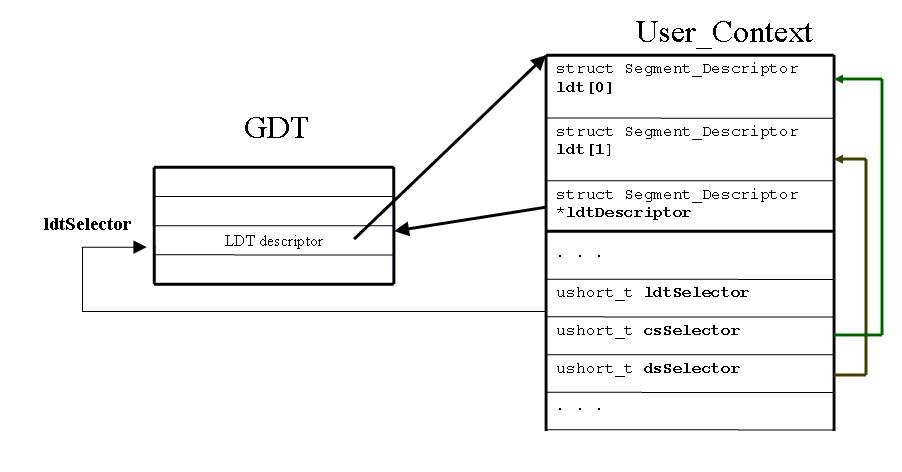
Descriptor Tables. The information describing a segment---which is logically a base address, a limit address, and a privilege level---is stored in a data structure called a segment descriptor. The descriptors are stored in descriptor tables. The descriptor tables are located in regular memory, but the format for them is exactly specified by the processor design. The functions in the processor that manipulate memory segments assume that the appropriate data structures have been created and populated by the operating system. You will see a similar approach used when you work with multi-level page tables in project 4.There are two types of descriptor tables. The Local Descriptor Table (LDT) stores the segment descriptors for each user process. There is one LDT per process. The Global Descriptor Table (GDT) contains information for all of the processes, and there is only one GDT in the system. There is one entry in the GDT for each user process which contains a descriptor for the memory containing the LDT for that process. This descriptor is essentially a pointer to the beginning of the user's LDT and its size.
Since all kernel processes are allowed to access all of memory, they can all share a single set of descriptors, which are stored in the GDT.
The relationship between GDT, LDT and User_Context entries is
explained in the picture below:

These registers do not contain the actual segment descriptors. Instead, they contain Segment Descriptor Selectors, which are essentially the indices of descriptors within the GDT and the current LDT.
The memory segments for a process are activated by loading the
address of the LDT into the LDTR and the segment selectors into the
various segment registers. This happens when the OS switches
between processes. If you like, you can follow the Schedule()
call in src/geekos/kthread.c to see how this is done (this will require
looking at some assembly code---beware!).